Fasteners
This section provides a whole host of examples of nails and screws, a comparison between nailing and screwing, screw guides and detailed advice on choosing the right screw in wood construction.
Nails
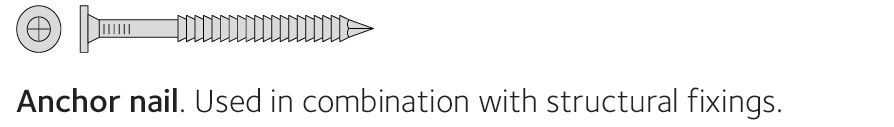
Nailing is traditionally the most common way to connect wood in buildings. There are all sorts of different nail types and grades. Screwing has increased in recent years, and is used today to fit sheet material and in load-bearing structures. Structural fixings are used in combination with nails or screws and allow for the transfer of forces.
For outdoor use, nails, screws and structural fixings must be protected against corrosion or made from stainless steel.
Things to consider before nailing:
- Will the nails be exposed to moisture?
- What is the substrate?
- What materials are to be fixed in place?
- Will the surface be filled or painted?
- Risk of causing splitting.
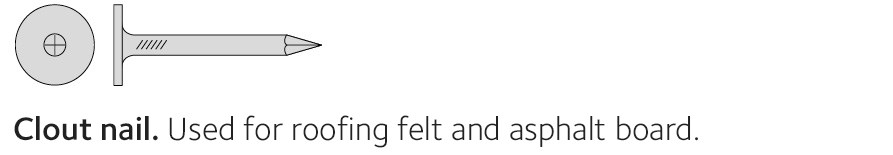
Always use hot-dip galvanised round wire nails when fitting exterior cladding, unless otherwise stated. Stainless steel nails are used in particularly exposed locations and to nail larch, thuja (Western red cedar) or pressure treated exterior cladding. Pre-drilling may be needed when nailing in groups, close to end-grain wood and into hard woods.
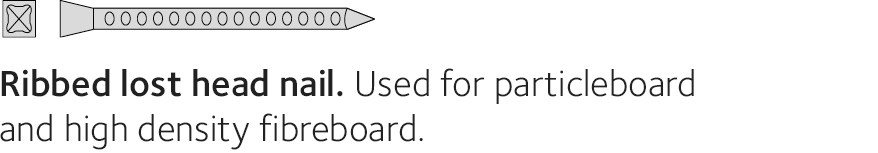
When nailing mouldings and suchlike that will also be filled and painted, lost head nails should be used. Always use lost head nails for secret nailing. Never mix different metals with each other, for example light metal nails on copper plate. Always use hot-dip galvanised nails outdoors and stainless steel nails and screws in particularly exposed locations. Hot-dip galvanising of greater than or equal to 50 μm (micrometres) equates to corrosivity class C4. Stainless steel grade A2 equates to corrosivity class C4, while A4 equates to C5.
Screws
Screws come in various shapes and sizes designed specifically to fix particleboard, plasterboard, mouldings, exterior and interior cladding, decking, structural fixings and floorboards. Screws for load-bearing structures may have a metric machine bolt thread or a wood screw thread. Screws are used for large-scale structures and to secure structural fixings. Specialist fasteners such as through bolts are used to assemble glulam structures.
Choice of screw
Thread
Partial thread: the shank nearest the head is not threaded (wood/particleboard/plywood). Full thread: (plasterboard).
Most common finish
Interior: electrogalvanised, phosphated, zinc yellow plated, white powder coated. Exterior: zinc/nickel C4, hot-dip galvanised, stainless, stainless/acid-proof.
Head
Flat: conical, often with ribs under the head to countersink the screw into wood/particleboard/plywood/MDF/HDF
Bugle: for interior plasterboard.
Screw drive
Slot, Philips, Pozidrive, square, hex, torx.
Point
Self-drilling: self-drilling screws do not require pre-drilling. Threaded point: for plasterboard and particleboard.
Fibre cut: used for hard materials such as particleboard.
Blunt: a nail point has a lower risk of spitting the wood than a threaded point.
Comparison between nailing and screwing
- Withdrawal forces are dealt with best by screws.
- Nails are softer than screws and can absorb small movements in the wood without it splitting.
- Disassembly is usually easier with screws.
- Avoid screwing or nailing closer than 100–150 mm from end-grain wood.
- If you do have to fix closer than 100–150 mm from end-grain wood
– pre-drill when nailing
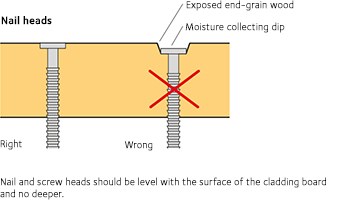
– use self-drilling screws when screwing. - Nailing exterior cladding with a nail gun should be avoided, since the nails can easily go too far into the boards, allowing moisture to penetrate around the nail head. This is also the case for screws that are driven in too far.
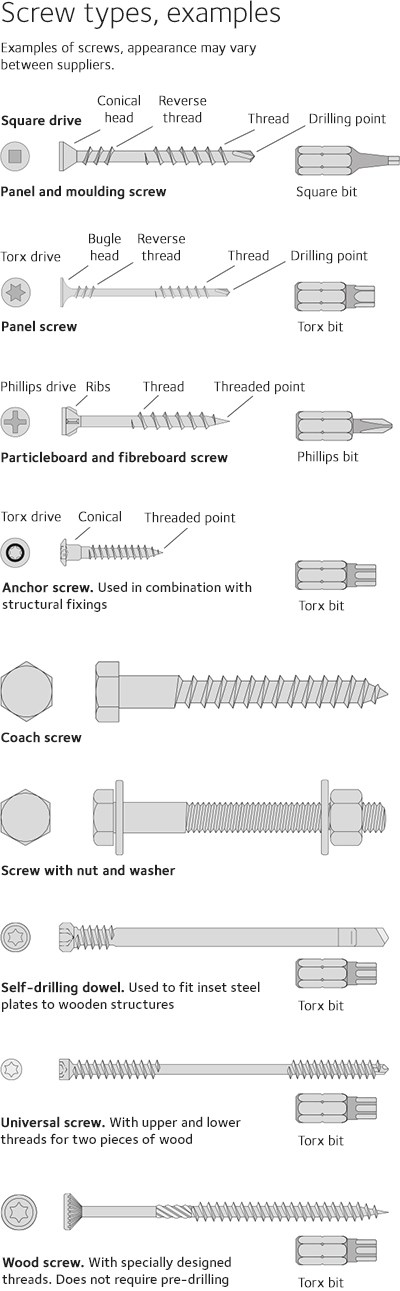
Screw types, examples
Examples of screws, appearance may vary between suppliers.
Find out more...
SS-EN 14545:2008 Timber structures. Connectors. Requirements. SIS Förlag AB, 2008.
SS-EN 14592:2008 + A1:2012 Timber structures. Dowel type fasteners. Requirements. SIS Förlag AB, 2012.
SS-EN ISO 1461:2009 Hot dip galvanized coatings on fabricated iron and steel articles. Specifications and test methods. SIS Förlag AB, 2009.
SS-EN ISO 12944-2 Paints and varnishes. Corrosion protection of steel structures by protective paint systems. Classification of environments. SIS Förlag AB, 1998.