Wood and wood-based products
Sawn timber, length packaged, is usually sold dried to the final moisture content relevant to the end use of the product. Many sawmills plane, profile, glue, finger-joint and pressure treat the timber themselves. More and more products are being refined into finished end products at the sawmills. Wood can be used for the manufacture of structural elements in all sorts of buildings, cladding products and joinery. Wood is also a key component of sheet material such as plywood, OSB, fibreboard and particleboard.
Wood for construction purposes
Wood for buildings can be divided into the following categories:
- Construction timber is used in load-bearing structures and is therefore subject to specific requirements concerning strength and stiffness.
- Cladding is used as a surface finish, as internal and exterior panelling, Other internal timber product uses are for floorboards, smooth planed timber and mouldings.
- Timber for formwork includes sections that are used for the structural elements with the relevant sheet materials to create shuttering for concrete castings.
- Scaffolding timber is used to create a safe structure and access for construction work to take place.
- Joinery timber arrives at the construction site in the form of various finished products such as windows, doors and interior mouldings.
Spruce is usually used for construction purposes. Planed interior products for cladding and internal joinery are usually supplied in pine.
The dimensional accuracy of the wood is improved through planing, known as dimension planing. Profiling is used for certain products, such as skirting and architraves.
The quality of the wood is usually specified via appearance grading in line with standard SS-EN 1611-1, see also the section Wood grades, according to a company-specific grading, or via strength grading of the wood.
Wood for buildings
Construction timber accounts for a significant proportion of the wood in buildings with a wooden structural frame. Specific developments and applications may require different requirements than those met by traditional grading.
Grades that are specified for construction timber are used for the load-bearing parts of a wooden building.
Dimension planed spruce products are primarily used for construction timber. Dimensions and qualities are tailored to different applications. The raw material is commonly sorted from grades G4-2 – G4-3.
Wood for civil engineering
Wood has become much more widely used in civil engineering in recent years, its many uses can include temporary structures, e.g. shuttering and scaffolding, and permanent structures such as acoustic barriers, jetties, footbridges, road bridges, posts and fencing.
Larger civil engineering projects often use glulam, while pressure treated timber is commonly used in structures that are exposed to the elements.
Construction timber
Strength graded wood is used for load-bearing structures. This grading may be conducted mechanically or visually in various classes, from C14 to C35. Finger-jointed timber may also be used as construction timber for load-bearing structures, with certain exceptions. Construction timber must be CE marked.
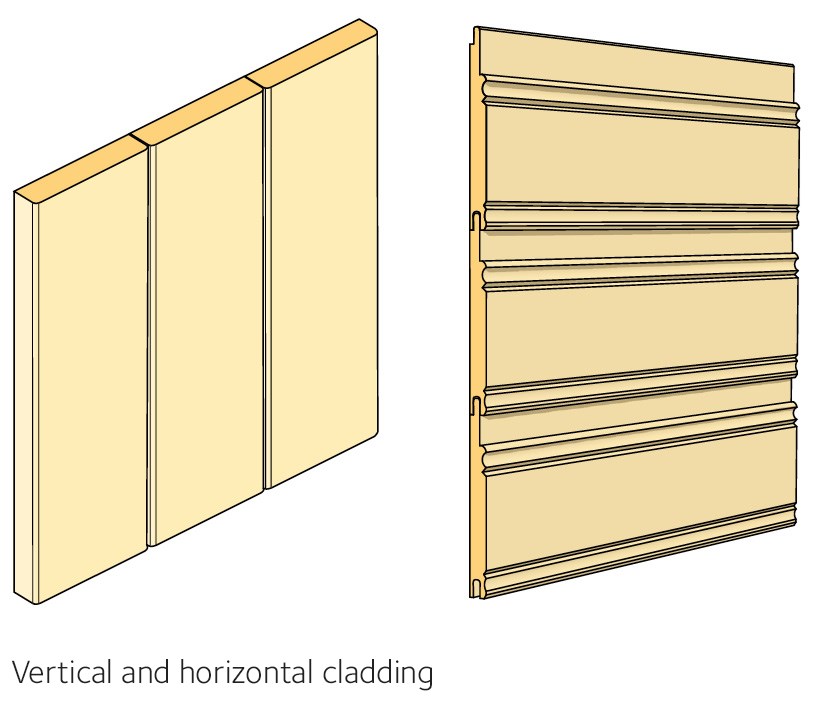
Cladding
Higher quality wood is usually used for cladding products, particularly if they will have an exposed surface. Both pine and spruce are commonly used internally, while spruce is used externally.
Exterior cladding
Resawn dried main yield spruce is used for exterior cladding boards. The wood grade should be G4-2 or better. Cladding with a fine sawn or grooved surface can be painted using most paint systems. If the surface is planed, the cladding should not be painted with distemper. To keep the surface free from splits, the cladding boards are resawn after the wood has been dried. A band saw does the resawing in conjunction with the profile planing. This creates cladding with good dimensional stability and a surface structure that is suitable for surface treatment. Exterior cladding must be CE marked.
Interior cladding
For interior cladding on walls and ceilings, pine or spruce of grade G4-1 or better should be used. Profile planing, for example tongue and grooving, rebating, chamfering or rounding, can create a wide range of different cladding types. Interior cladding must be CE marked.
Smooth planed
Smooth planed timber is manufactured from pine of at least grade G4-1.
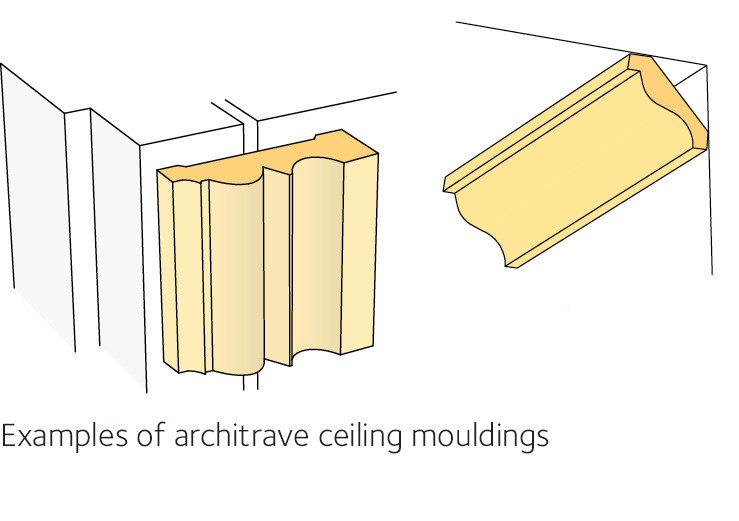
Mouldings
Mouldings made from solid wood are available in a wide range of different profiles and dimensions. In the Swedish standard SS 232811, mouldings are divided according to use into types A and B. Finger-jointed timber may occur in type B. In this case though, the fingers are shorter and are visible on the flat face of the moulding.
Type A mouldings are high quality, made from pine or hardwood, and are mainly intended for transparent treatment. The wood for the mouldings must be straight grown, free from splits, blue stain, pith streaks and pitchwood, and it must not be finger-jointed or repaired. Some sound knots, max. 7 mm in size, are permitted. Knots must not take up more than a third of the moulding’s width.
Type B mouldings are mainly those intended for painting and those intended for transparent treatment where knots are acceptable as a natural feature. The wood must be free from deep splits and pitchwood. Other splits with a width of max. 0.5 mm are permitted. Wood for mouldings must not be finger-jointed or repaired with wooden plugs. The size of the knots must not exceed a third of the moulding’s width. Knots other than sound knots are not permitted. Type B mouldings are not recommended for mouldings with a thickness of less than 10 mm.
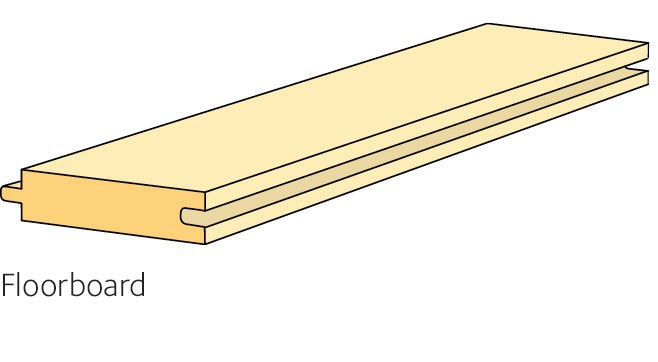
Floorboards
Floorboards in solid coniferous wood are made using both pine and spruce. The grade and appearance varies between different flooring manufacturers. Tongue and groove floorboards are produced in grade G4-2 or better. The main yield is usually used, which means that larger or smaller streaks of heartwood will be visible in the surface of a pine floor.
It is important that the floorboards which are to form a decorative or seen surface should have been kiln dried to and maintain a carefully tailored moisture content, typically 8%, and that they are not laid until the climate in the building is the equivalent of the end use stage. This is in order to avoid unnecessary tensions or movement in the floor. Wood for flooring must be CE marked, see also section Wood and moisture.
Formwork
The wood used for concrete shuttering is usually of a lower appearance grade, G4-4 or better, than the wood used as construction timber. It is common to have a sawn surface facing the concrete. Construction timber is used for the load-bearing parts of the shuttering.
Scaffolding timber
Scaffolding uses timber that meets the requirements for construction timber. Pre-used wood may be used. Scaffold boards must not be finger-jointed. Sawn timber is used to reduce the risk of slipping when walking on the surface.
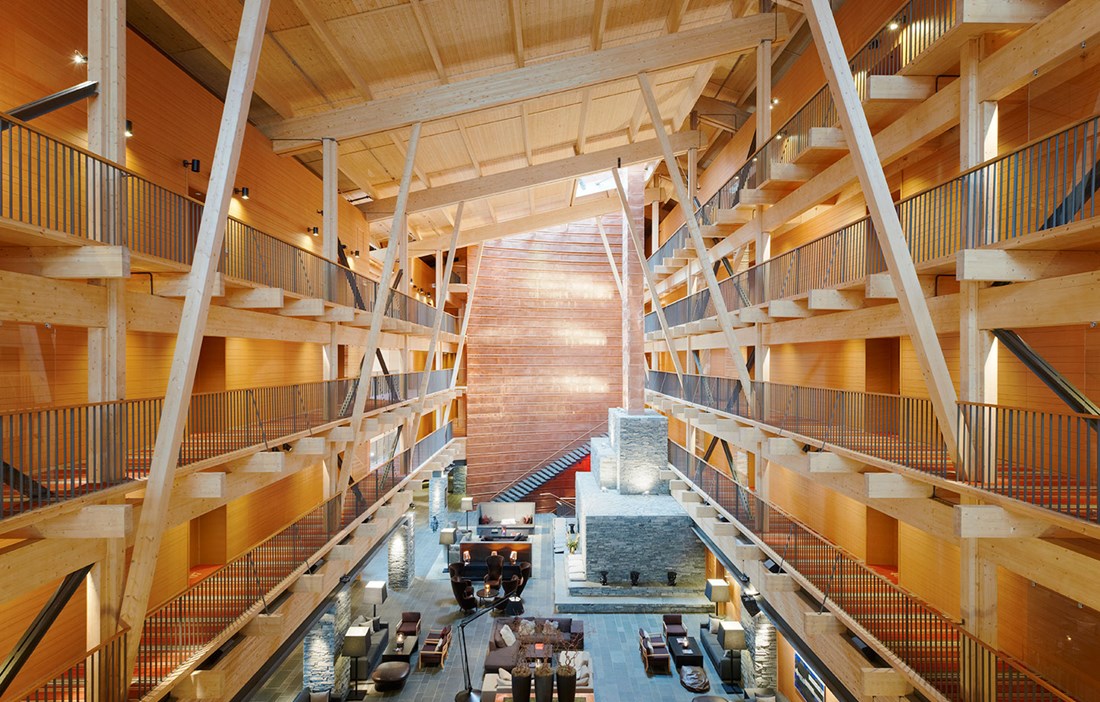
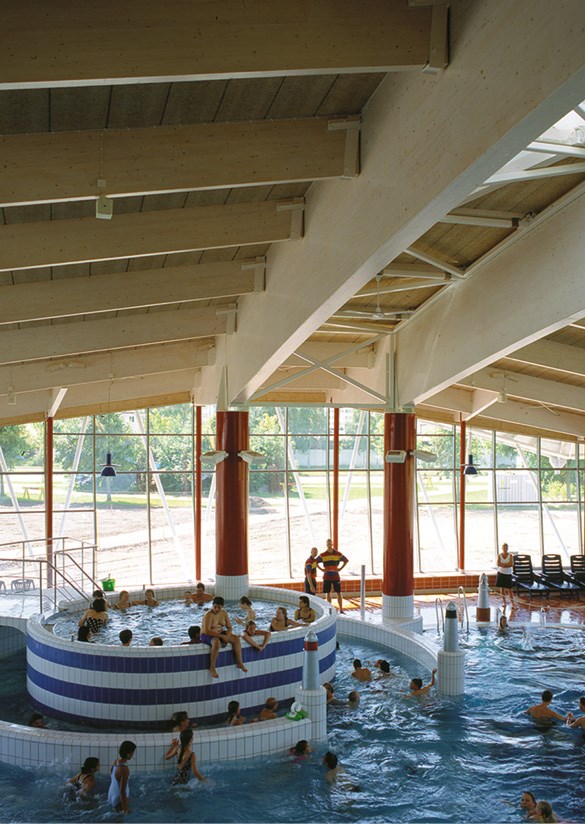


 Glulam in Sannarpsbadet, Halmstad. Photo: Garry Johansson.
Glulam in Sannarpsbadet, Halmstad. Photo: Garry Johansson. Summerhouse, Husarö, nominated for the Swedish Timber Prize 2008. Photo: Åke E:son Lindman.
Summerhouse, Husarö, nominated for the Swedish Timber Prize 2008. Photo: Åke E:son Lindman. Summerhouse, Husarö, nominated for the Swedish Timber Prize 2008. Photo: Åke E:son Lindman.
Summerhouse, Husarö, nominated for the Swedish Timber Prize 2008. Photo: Åke E:son Lindman. Barn with glulam structural frame. Löhammar Barn, Östhammar, nominated for the Swedish Timber Prize 2008.
Barn with glulam structural frame. Löhammar Barn, Östhammar, nominated for the Swedish Timber Prize 2008.



